Apricot was often called the "Armenian apple", although its origin was not reliably established. In Armenia, it has been grown since ancient times and is considered one of the national symbols. The life expectancy of an apricot tree in a warm climate reaches 100 years, of which 30-40 years it abundantly bears fruit and delights with its delicious, aromatic fruits. Apricot varieties have also been bred for other regions. In each of them, a tree can produce a decent crop, but proper agricultural technology is important for this. The first and one of the most important moments of it is the planting of a seedling.
Apricot planting dates
Apricot is best planted in early spring, always with sleeping buds. Planting with open buds can kill the plant.

Apricot seedlings can be planted in spring until buds are awakened
Keep in mind the climate of your region. Landing is possible in the southern regions at the end of March, in central Russia - in mid-April. The main condition is air heating above zero temperature, not only in the daytime, but also at night.
If planted earlier, the plant may die from return frosts. A late planting will negatively affect the survival rate of a seedling due to increased activity of the sun.
Advantages of spring planting apricot:
- the possibility of the formation of a powerful root system before autumn frosts and, as a result, a good wintering of the plant;
- timely elimination of negative factors: diseases, pests, drought, which improves the development of the seedling and increases its immunity;
- the possibility of preparing the pit for landing in advance. The preparation of the pit in the fall eliminates the risk of deepening of the root neck due to good subsidence of the soil during the winter.
The main disadvantage of spring planting is a short period of time between spring frosts and the awakening of the buds. It is not always possible to catch this moment and land on time.
And yet, most gardeners prefer spring planting, given the heat-loving culture.
However, there is the possibility of planting apricot in the autumn, mainly in the southern regions with warm winters and a long transition period with rather high temperatures in the autumn months.
The advantages of autumn planting:
- a wide selection of planting material, reasonable prices, the ability to assess the condition of the roots;
- a large amount of necessary moisture after planting - nature itself provides a seedling, it does not need increased attention and care.
If the plant is planted on time, it manages to take root before frost and starts to grow early in the spring and develops faster.
Disadvantages of planting in the fall:
- in winter, young plants can suffer from natural factors: ice, strong winds, snowfall, severe frosts;
- seedlings in winter damage rodents.
Experts do not recommend planting apricot varieties in autumn that do not have good winter hardiness.
How to prepare for landing
In order for the apricot to bear fruit, it is necessary to plant 2-3 seedlings of different varieties, since most varieties require cross-pollination. If there is no such possibility, it is necessary to plant self-fertile varieties, for example, Krasnoshcheky.
Choosing a landing place
Apricot loves light and heat, does not tolerate drafts and shading. Under suitable conditions, the tree grows large, with a spreading crown. In the lowland, it is not worth planting because of the accumulation of cold air and the possibility of stagnation of water, which can lead to the death of the plant. If possible, it is better to plant it on a hill, a hillside.

In favorable conditions, you can get a good crop of apricots
Of the cardinal points, the western, southwestern and northwestern are preferred. The northern part of the site, fenced off from the winds, is also a favorable place for landing.
Soil requirements
The soil for apricot should be light, loamy or sandy loam, with a sufficient amount of chernozem and minerals.
The acidity of the soil is neutral or slightly acidic. Fertilizers with a phosphorus content of 0.10-0.12 kg per 1 m² are added to clay soil.
Neighbors in the site
When choosing a landing site, you need to consider that the apricot does not like the neighborhood with other trees, especially this applies:
- cherries
- apple trees
- peach
- walnut
- sweet cherries
- pears
- raspberries
- currants.
When planting an apricot next to a plum, a distance between them of at least 4 m is necessary so that they do not oppress each other.
Landing pattern and preparation of the landing pit
Apricot trees are planted in a checkerboard pattern with a distance between trees and between rows of at least 3-4 m, since the tree is very spreading.
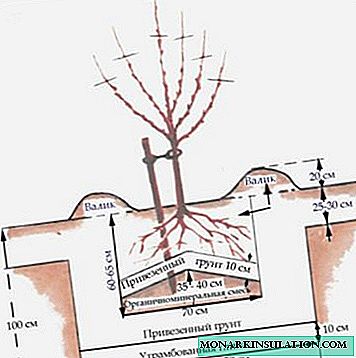
It is better to prepare a pit for planting an apricot in the fall or at least a week before planting. The dimensions of the pit are 70 × 70 × 70 cm.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- A drainage "pillow" of crushed stone, gravel or small pieces of brick is poured at the bottom. It is needed to protect the tree from excess moisture.

Drainage "pillow" is needed to protect the roots of the apricot seedling from stagnation of moisture
- Soil is laid on top of the drainage as part of:
- the top layer of the earth - 1.5 parts;
- humus leaf - 5 parts;
- Mullein - 1 part;
- wood ash - 60 g;
- superphosphate - 50 g.
- All this is well mixed and covered with garden soil from above to prevent direct contact with the roots of the seedling.

After laying the fertile layer, the pit under the apricot is covered with previously removed garden soil
As soil, you can use a mixture of sand, peat and earth in equal parts. The main thing for apricot is the looseness of the soil, and not its composition.
How to plant an apricot so that it successfully bears fruit
When planting in spring and autumn, you need to follow a certain sequence in order to get a good harvest:
- Soak the roots of the seedling in water a day before planting.

Soaking the roots is only necessary for apricot seedlings with an open root system
- Check the condition of the roots and trim the damaged ones.
- Dip the roots of the seedling in a clay mash with manure and dry them a little. Heteroauxin can be added to the talker to improve survival.
- Make a tubercle from the ground in the center pit.
- Put the seedling in the center and spread the roots well, while the root neck should be above the level of the pit.

When planting an apricot seedling, it is important to spread the roots well, for this a mound from the ground is first poured into the pit
- It’s not necessary to fill the roots with earth; you don’t need to fill the neck of the trunk with earth. Tread the ground gently around the seedling. To put a foot toe to a trunk, and to trample a heel.
- At the edges of the pit, make a watering circle, protecting the neck with a mound.
- Pour seedlings abundantly with water over the irrigation circle, preventing water from getting under the trunk.

Apricot seedling must be watered in the irrigation circle so that water does not get on the root neck
- Snap the seedling to the peg in two places.
After planting, the seedling should stand evenly and firmly sit in the ground.
Video: planting an apricot seedling
Winter seedling storage
What if the seedling could not be planted in the fall? There are different ways to keep it until spring.
In the cellar
In the cellar or garage, apricot seedlings can be stored at temperatures from 0 to +10 ºC. The roots are moisturized, placed in a container with sawdust, sand or peat and put in a cool place. The container needs to be moistened about once a week.

When storing apricot seedlings in the cellar or garage, it is worth signing each grade
Snowing
This method is used in snowy areas (snow thickness should be at least 15 cm). So that the seedlings are well preserved, that is, do not freeze and soprel, they do this:
- Before snowing, they are kept in water for 5 hours and leaves are removed.
- Then they select the most snow-covered plot in the garden, where there is less sun, and prepare a hole, leaving a snow "pillow" with a thickness of 15-20 cm.
- Apricot seedlings packed in burlap or agrofiber are laid in a prepared pit. You can arrange them vertically, thus saving space.

Apricot seedlings are placed horizontally on a snowy "pillow"
- Horizontally placed plants are covered with a layer of snow 10-15 cm thick and then with a layer of sawdust or wood shavings of the same thickness. Vertically standing apricot seedlings are covered with snow by two-thirds.

Vertically located apricot seedlings should be covered with snow for a maximum of two thirds
In a snow pit, seedlings are stored until spring in conditions that are comfortable for them.
Digging in the ground
Sapling is added apex to the south in an inclined position. For this:
- Dig a ditch in the direction from west to east with a shallow south side and a vertical north wall.

A ditch for digging seedlings is dug in a direction from west to east
- Before digging from the seedlings, they cut off all the leaves for a better wintering.
- Then the seedlings are coated with liquid clay and sprinkled with earth. Plants with the name of the variety, written with a marker on plastic or aluminum, must be attached to the plants.
- Plants are laid in a ditch sloping crowns to the south at a small distance from each other. This arrangement reduces exposure to cold northerly winds and prevents sunburn.

Apricot seedlings are laid in a ditch under the slope of the crowns to the south.
- Apricots are covered with soil 20 cm above the root neck.
- The earth is tamped with a shovel.
- Behind the first row, lay the second in the same direction.
With the onset of frost on the soil, the ground groove with seedlings must be covered with dry earth or its mixture with sawdust - completely, with the formation of a knoll.

The groove with seedlings is covered with dry earth or its mixture with sawdust until a hill is formed with the beginning of frost on the soil
The branches can be covered with prickly rose hips or blackberries to protect against rodents and frosts. In winter, it is advisable to throw a mound with snow. Snow flaking and instillation require protection from rodents also using pesticides. The baits are laid out in tin jars in an inclined position so that in the spring it was possible to remove unused poison and it did not hit the ground.
Video: dripping apricot seedlings
Unconventional methods of planting apricot
Apricot planting options may vary depending on soil, climate, and other factors.
On the sand
If the soil on the site is sandy, and you need to plant an apricot, you should not worry.
Sand is light soil, has good breathability and is quite suitable for growing apricot. But there are significant disadvantages. Such soil does not hold water well, nutrients are washed out, and become inaccessible to the plant.

Sandy soil is quite suitable for planting apricot, as it is light and water permeable
In order to improve the structure of the soil and ensure water retention, clay is poured on the bottom of the pit with a layer of 10-12 cm. The pit is filled with soil with a high content of humus, which consists of the following elements:
- sand - 1 part;
- turf land - 2 parts;
- compost - 2 parts.
On sandy soils, apricot requires more frequent watering during fruit ripening and regular application of organic fertilizers, excluding fresh manure and chicken droppings.
If you need to plant an apricot seedling in loose sand, then do so:
- At first they dig a hole much more than is necessary for placing the roots: it is dug 1.5-2 m wide and 1 m deep.
- Clay is poured into the bottom of the pit, as described above, then it is covered with imported fertile soil, thus cultivating the soil. If the soil brought in is heavy, clayey, it is mixed at 35-40% with sand dug from the pit, and peat in the amount of 10-15% is added.
When planting apricot on sandy soil, clay and peat are added to the pit
- In the center of the prepared pit, they then make the usual landing pit.
When the trees grow, on the 4th-5th year outside the pit they dig ditches up to 70 cm in width and depth, and fill them with the same fertile imported soil, expanding the cultivated layer for further root development.
According to the method of Zhelezov
Valery Konstantinovich Zhelezov, an outstanding gardener from Sayanogorsk, has long and successfully grown apricots in his homeland in Siberia. The plant should be planted as early as possible, immediately after the end of the frost, in order to have time to mature before winter.
Zhelezov advises to plant apricot in this way:
- Put the seedling for 1 night in cold rain or melt water in a dark, cold room.
- Make a seat in the garden - a gentle hill with a diameter of up to 2 m and a height of 20 to 50 cm (for snowy areas). The hill makes it possible to warm the soil early in the spring. This will protect the root neck and trunk from decay.

A gentle hill when planting a seedling allows early heating of the soil in spring
- Make a hole in the center according to the size of the straightened roots. Fertilizers do not need to be applied.
- Trim the seedling at least half the crown.

Pruning an apricot seedling will allow it not to spend a lot of effort on maintaining a large amount of green mass in the first year of life
- Place the seedling in the hole so that the root neck is strictly on the border with the ground, and fill it with soil.
- Scatter on top of the fertilizer at a distance of half a meter from the seedling stock.
- Close the seedling with a 5 liter bottle with a cut bottom for 1 month. This will allow him to fully mature in a short Siberian summer.

Shelter of apricot seedling with a plastic bottle will allow it to fully ripen in a short Siberian summer
- Seek undersized grass or mowed grass, leaving it in place after mowing.
Planting two apricot seedlings in one pit
Apricots, like other fruit trees, can be planted with nests - 2 or more plants in one hole, regardless of region. This type of landing has many advantages:
- plants suffer less from frost and sunburn;
- more snow accumulates near them in winter, which improves the conditions of wintering and growth. In spring, it is necessary to remove snow from the trunks;
- when one of the plants dies as a result of exposure to unfavorable factors, the second one can survive and begin to develop better due to the preservation of the roots of the deceased as a result of their growth.
- nesting allows to reduce the area occupied by plants, and increase productivity due to mutual pollination.
The planting pit for two apricot seedlings should have a diameter of at least 100 cm, the distance between the seedlings when planting is 30-40 cm. Pit preparation and planting are carried out according to the standard, as well as one seedling.
Nesting is best done on elevations (hills, high ridges, etc.) for better ventilation and elimination of stem breeze, which leads to the death of the plant.
Features of planting apricot in various regions
In each region, zoned apricot varieties are used for planting. The timing of planting this culture is also different:
- in the Volga region (for example, in the Volgograd region) apricot planted since the end of March;
- in central Russia and the Moscow Region, landing is carried out no earlier than the last days of April;
- in the Urals and Siberia, apricot planting is possible not earlier than the end of April and only the northern varieties. Planting is recommended in high places. When returning frosts, seedlings are covered with non-woven material.

In Siberia, it is recommended to plant apricots in high places
In any region, in the spring it is necessary to remove snow from the trunk. At the time of fruit setting, watering is necessary if there is no rain.
Varieties for Siberia are frost-resistant:
- Amur is a frost-resistant table variety with an average ripening period, high-yielding, obtained at the Far Eastern Research Institute of Agriculture in 1950-1960.Included in the State Register for the Far Eastern region in 1979;
- Seraphim - Received at the DalNIIISH G.T. Kazmin. The fruits are tasty, early ripening, high productivity. He does not like high humidity;
- East Siberian - received in the Republic of Khakassia I.L. Baykalov in 1981, was included in the State Register in 2002 for the East Siberian region. A very early variety with large fruits, not resistant to aging;
- Primorsky (Krasnoshchekiy) - obtained at the Far Far Agricultural Research Institute, the ripening period is medium, the fruits are large, sweet. Winter-hardy and fruitful.
Apricot transplant
Apricot transplantation has its own characteristics, which you need to know about so that everything goes well and the tree takes root.
There is an opinion that the apricot, transplanted three times, turns from a wild game into a cultural species. This is not true. He will remain a wilderness until he is vaccinated, but his life span will be reduced with each transplant. The transplantation negatively affects the state of the fruit tree - the roots are damaged, the margin of safety is reduced.
You can transplant the plant in spring and autumn:
- spring apricot transplant is carried out during the period of a sleeping state, before the buds swell:
- plus is sufficient soil moisture and heat, which provides quick survival in a new place;
- minus - the need for frequent watering and the risk for the plant to be unprepared for winter cold;
- Autumn transplant may be better for rooting the plant. The main thing is that it has time to take root before the frost. It should not be delayed with a transplant in the fall.
Apricot transplantation is highly undesirable to be performed repeatedly; ideally, only one transplantation is possible if necessary. The age of the transplanted tree should not exceed 6-7 years.
The technology for transplanting an adult apricot is as follows:
- In the fall, a landing pit is prepared with a diameter of almost twice the size of the tree crown. The pit is prepared in the usual way with the device of a drainage pillow and the introduction of soil mixed thoroughly with fertilizers.

Apricot transplant pit should be twice as large as crown diameter
- 3 hours before transplanting, apricot is abundantly watered.
- Dig a tree along the diameter of the crown to a depth of 80 cm.
- With a few shovels or pitchforks they lift a lump with a tree and roots and move it to the cooked burlap.

Sacking is needed so that the earth does not crumble from the roots
- The lump is wrapped in burlap and bandaged to preserve its integrity.
- They put a tree with a lump of earth in a prepared hole and fall asleep, crushing the earth a little.
- Make a roller around the barrel for irrigation.
- The crown is trimmed a little to make it easier for the roots to handle the load.
The aroma of apricot fruit, its excellent taste and benefits are of constant interest to amateur gardeners in all corners of the earth. It is grown even in Siberia, and not without success. Indeed, most apricot varieties are frost-resistant, can withstand frosts down to -30 ° C, and in hot regions they are not afraid of drought.



























